Description
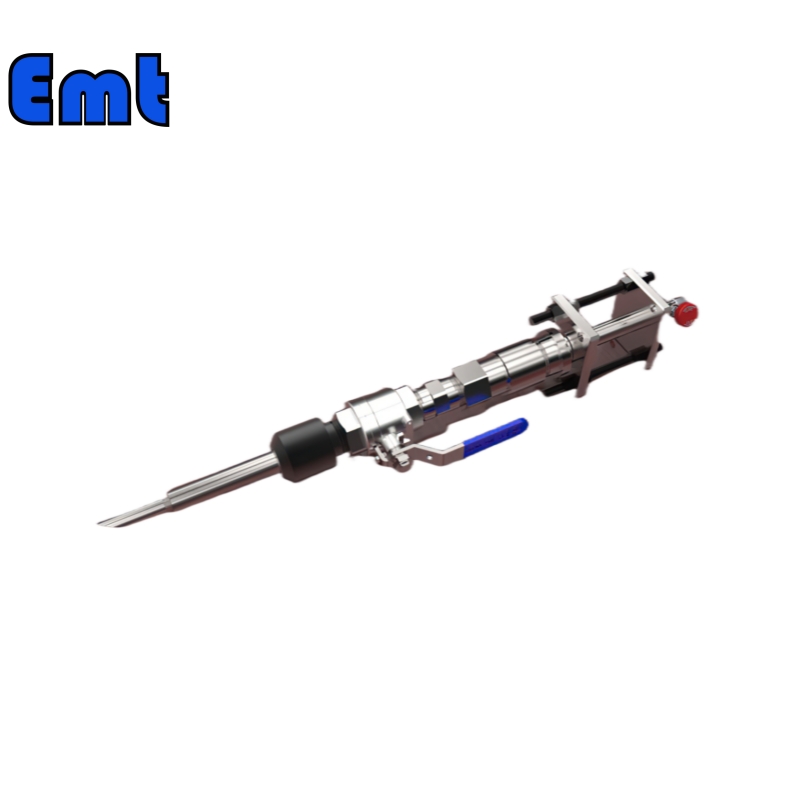
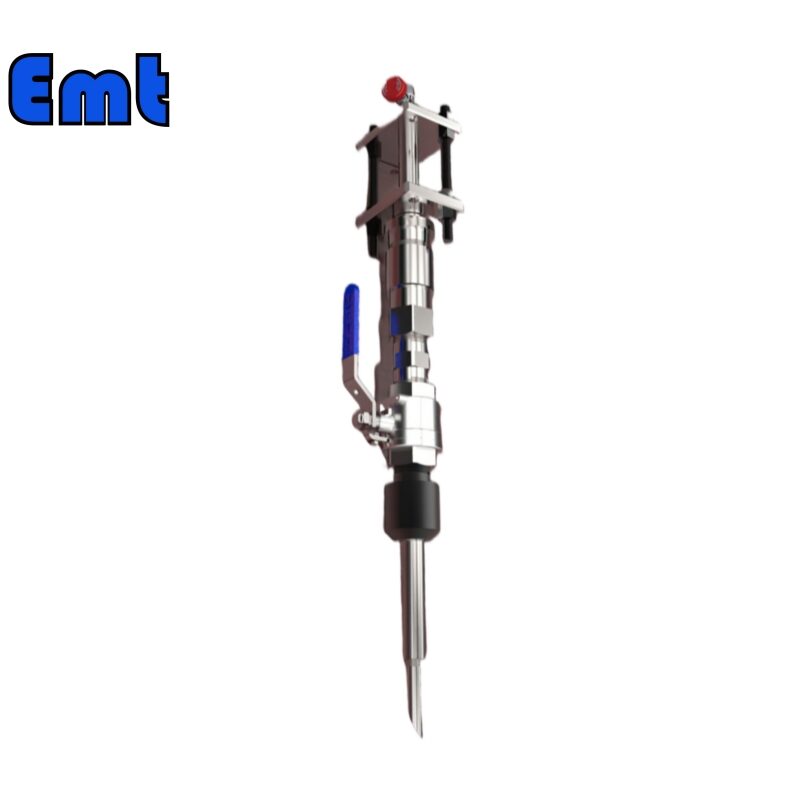
Introduction to Injection Quill With Check Valve
An injection quill with a check valve offers precise chemical injection into pipelines. It ensures the efficient distribution of chemicals. The check valve prevents backflow, enhancing system safety. Therefore, it protects the injection source from contamination. It is very simple to install, so it is easy for users to use. In addition, it can handle a variety of chemicals and flow rates. It has a wide range of applications. Proper use improves chemical treatment effectiveness. Therefore, the performance and longevity of the system can be optimized by it.
How Does a Check Valve Work?
Cracking Pressure
A check valve requires a minimum upstream pressure to open. This minimum upstream pressure is called the valve’s “cracking pressure.” The pressure differential between the inlet and outlet must meet this threshold. Different valve designs and sizes have varying cracking pressures. Ensure the system’s pressure can generate the necessary cracking pressure.
Closing
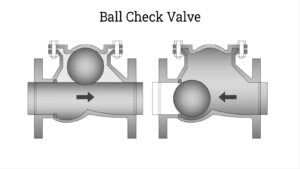
If upstream pressure falls below the cracking pressure the valve will close. Back pressure also causes the valve to close. Typically, a gate, ball, diaphragm, or disc closes the valve. Gravity or a spring can assist in this process. As inlet pressure decreases, the valve closes via gravity, spring, or back pressure.
Installation Orientation
Proper installation orientation is crucial since a check valve allows flow in only one direction. An arrow on the valve’s housing usually indicates the flow direction. If there isn’t an arrow, inspect the valve carefully. Incorrect installation prevents media from moving and may cause pressure build-up. This build-up can damage the system.
Normally Open and Normally Closed Check Valves
A normally open check valve allows free flow but shuts off in case of backflow. Instead, a normally closed check valve prevents fluid flow until rupture pressure builds up. At this point, the valve opens. Understanding these types helps in selecting the right valve for your system.
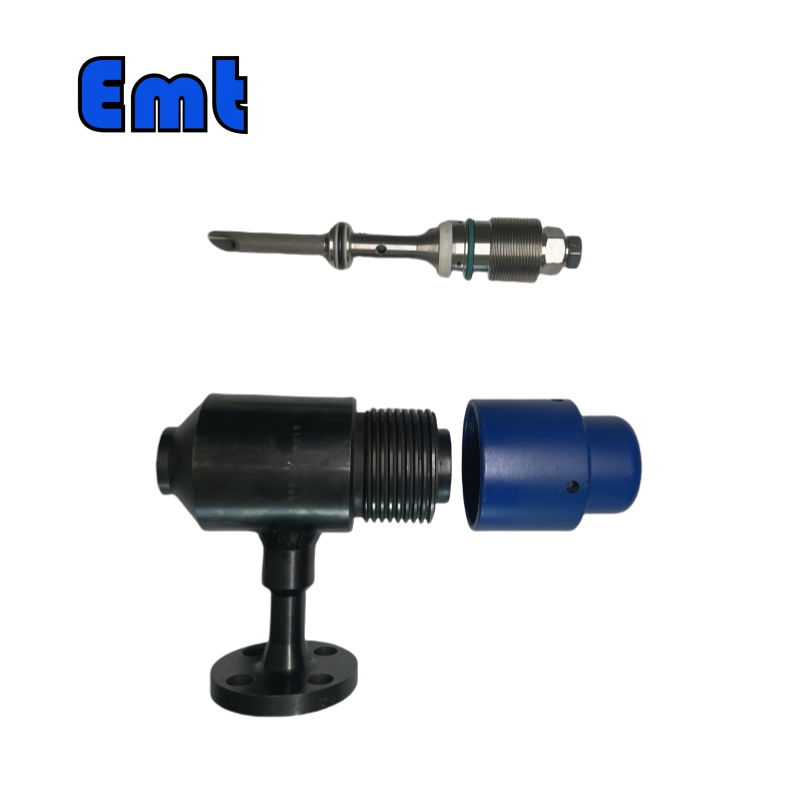
Nozzle Types of Chemical Injection Quills
Chemical injection quills come with various nozzle types to suit different applications:
- Parallel Nozzle: Directs the chemical flow parallel to the pipeline. This design ensures smooth blending with the main flow.
- Perpendicular Nozzle: Injects chemicals at a 90-degree angle to the pipeline. It promotes thorough mixing by creating turbulence.
- Open Nozzle: Lacks directional control, allowing chemicals to disperse freely. It is ideal for applications needing broad distribution.
- Sampling Nozzle: Designed for extracting samples from the pipeline. It allows for accurate monitoring of chemical concentration and effectiveness.
Selection Model of Injection Quill With Check Valve
| Model | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SI | Chemical Injector Quill | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -Code | Plug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pxxx | Type | Material | Sealing Material | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | No Request | 0 | CS | 0 | No Request | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | Hollow Plug Body | 1 | 316SS | 3 | DSS | 1 | Viton O-Ring / PTFE Primary Packing | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | Solid Plug Body | 2 | 316LSS | 4 | INCONEL | 2 | HNBR | ||||||||||||||||||||
| – Code | Injection Nut | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nxx | Connection Size | Material | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | i.e. No Request | 0 | i.e. CS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | i.e. 1/4″ | 1 | i.e. 316SS | 3 | i.e. DSS | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | i.e. 1/2″ | 2 | i.e. 316LSS | 4 | i.e. INCONEL | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| – Code | Injection Tube | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sxxx-Lx″ | Connection Size | Material | Nozzle | Line size(x″) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | No Request | 0 | CS | 0 | i.e. No Request | The most effective position for injection is generally at the center of the pipe | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | i.e. 1/4″ | 1 | i.e. 316SS | 1 | i.e. Open | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | i.e. 1/2″ | 2 | i.e. 316LSS | 2 | i.e. Quill | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | i.e. DSS | 3 | i.e. Cap & Core | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | i.e. INCONEL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| – Code | Nipple and Valve(or end Flange)of Tee | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Txx | Connection Size | Material | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | i.e. No Request | 0 | i.e. CS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | i.e. 1/4″Nipple | a | i.e. 1/4″Nipple and Valve | 1 | i.e. 316SS | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | i.e. 1/2″Nipple | b | i.e. 1/2″Nipple and Valve | 2 | i.e. 316LSS | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | i.e. 3/4″Nipple | c | i.e. 3/4″Nipple and Valve | 3 | i.e. D SS | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | i.e. 1″Nipple | d | i.e. 1″Nipple and Valve | 4 | i.e. INCONEL | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | i.e. 1/4″Flange | e | i.e. 1/4″Nipple end Flange | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | i.e. 1/2″Flange | f | i.e. 1/2″Nipple end Flange | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | i.e. 3/4″Flange | g | i.e. 3/4″Nipple end Flange | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8 | i.e. 1″Flange | h | i.e. 1″Nipple end Flange | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| For Example, SI-P221-N12-S122-L4″-T22 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Parameters of Injection Quill With Check Valve
| Name | Pipeline Chemical Injection Quill Sampling System |
| Material | Stainless Steel 304、Stainless Steel 316、DSS F51、Carbon Steel A105N、Inconel 625 |
| Operating Temperature | -20±120 |
| Feature | 1. Easy Operating |
| 2. High Accuracy Long Life | |
| 3. High Efficiency, Low cost | |
| Payment | TT/LC |
| Advantage | Firstly, they are lightweight and flexible. |
| Secondly, nice Injection efficiency. | |
| At last, accurate location tracking. |







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.